
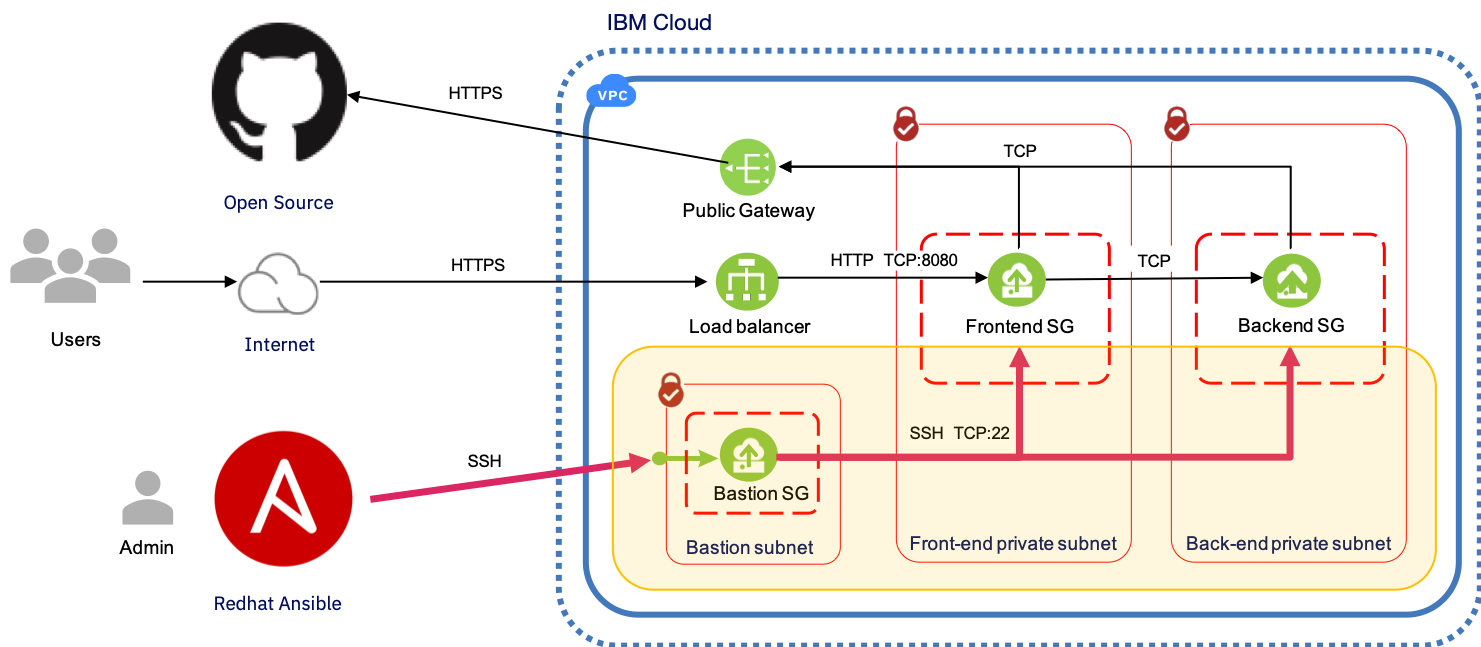
You cannot modify or delete these routes. If you’ve associated an IPv6 CIDR block with your VPC, your route tables contain a local route for the IPv6 CIDR block. A route table that contains a local route for communication within the VPC over IPv4.When you create a custom VPC, AWS automatically creates: Amazon recommend you specify a CIDR range from the private (non-publicly routable) IP address ranges as specified in RFC 1918. You can’t change the size of a VPC after you create it. The allowed block size is between a /28 netmask (16 IP addresses) A VPC can be assigned at most 1 IP address range at any given time.ĬIDR notation is a syntax for specifying IP addresses and their associated routing prefix in the format 10.0.0.0/28. When you create a custom VPC within an AWS region, you specify the IP address range in the form of a CIDR block. Associate the default DHCP options set for your AWS account with your default VPC.īy default, a default subnet is a public subnet, because the main route table sends the subnet’s traffic that is destined for the internet to the internet gateway.Create a default network access control list (ACL) and associate it with your default VPC.Create a default security group and associate it with your default VPC.Create an internet gateway and connect it to your default VPC.This provides up to 4,096 addresses per subnet, a few of which are reserved for our use. Create a size /20 default subnet in each Availability Zone.This provides up to 65,536 private IPv4 addresses. Create a VPC with a size /16 IPv4 CIDR block (e.g.When we create a default VPC, we do the following to set it up for you: The default VPC is user friendly, allowing you to immediately deploy instances. Egress-only Internet Gateway: A stateful gateway to provide egress only access for IPv6 traffic from the VPC to the Internet.VPC Endpoints: Enables private connectivity to services hosted in AWS, from within your VPC without using an Internet Gateway, VPN, Network Address Translation (NAT) devices, or firewall proxies.
Peering Connection: A peering connection enables you to route traffic via private IP addresses between two peered VPCs.Virtual private gateway: The Amazon VPC side of a VPN connection.NAT Gateway: A highly available, managed Network Address Translation (NAT) service for your resources in a private subnet to access the Internet.Internet Gateway: The Amazon VPC side of a connection to the public Internet.Subnet: A segment of a VPC’s IP address range where you can place groups of isolated resources.You define a VPC’s IP address space from ranges you select. A Virtual Private Cloud: A logically isolated virtual network in the AWS cloud.You can leverage multiple layers of security, including security groups and network access control lists, to help control access to Amazon EC2 instances in each subnet.Īdditionally, you can create a Hardware Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection between your corporate datacentre and your VPC and leverage the AWS cloud as an extension of your datacentre.Īmazon VPC comprises a variety of objects that will be familiar to customers with existing networks:

For example, you can create a public-facing subnet for your web servers that has access to the Internet, and place your backend systems such as databases or application servers in a private-facing subnet with no Internet access. You can easily customize the network configuration for your Amazon VPC. You can use both IPv4 and IPv6 in your VPC for secure and easy access to resources and applications. You have complete control over your virtual networking environment, including selection of your own IP address range, creation of subnets, and configuration of route tables and network gateways. Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (Amazon VPC) lets you provision a logically isolated section of the AWS Cloud where you can launch AWS resources in a virtual network that you define.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
